Determinants of Household Waste Management Behavior within the Fourth Pillar of Community-Based Total Sanitation (STBM) in Indonesia
Downloads
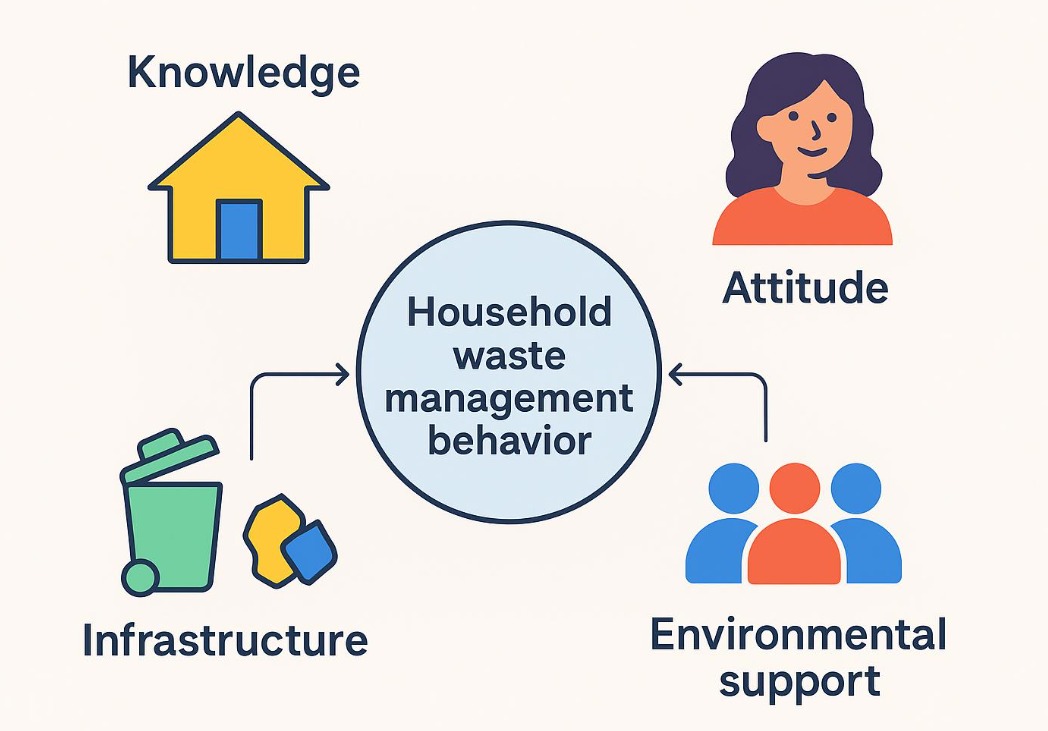
The 4th pillar of the Community-Based Total Sanitation (STBM) program emphasizes household waste management, which is crucial due to the significant contribution of household waste to environmental pollution. This study aimed to analyze the influence of knowledge, education, and triggering on the implementation of the 4th pillar of STBM in Mojosulur Village, Mojosari District, Mojokerto Regency in 2025. An analytic observational design with a cross-sectional approach was applied, involving 92 housewives selected through systematic random sampling. Data were collected using questionnaires to measure knowledge, education, and triggering experience, and observation sheets to evaluate household waste management practices. The results showed that the overall implementation of the 4th pillar of STBM was still low, with only 15.2% of households practicing proper waste management. The Chi-Square test indicated that knowledge had no significant association with STBM 4th pillar implementation (p = 0.109), while education (p = 0.004) and triggering (p = 0.000) were significantly associated. These findings highlight that higher education and structured triggering activities play a key role in strengthening household waste management. Local governments and environmental health officers are recommended to intensify triggering interventions and strengthen community education programs, focusing on the three main components of STBM enabling environment, increasing demand, and increasing supply to promote sustainable waste management behavior at the household level.
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Alfatih Dimas Rusadi, Winarko, Suprijandani, Fitri Rokhmalia, Yenni Dwi Kurniawaty

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.